Brain activity has traditionally been assessed using large and often expensive technology that has limited its use to specific clinical settings. Small wearable devices that can assess brain activity show promise for improving the diagnosis and monitoring of brain diseases like dementia or depression. In a study published recently in Advanced Materials Technologies, researchers from Osaka University have developed a wearable device that is unobtrusive and comfortable, which can measure brain activity in everyday situations—and its technology may potentially monitor many other health indicators as well.
Unlike other health-related measurements that can be taken at home, such as blood pressure or weight, brain activity currently needs to be evaluated by highly trained medical staff using bulky and expensive equipment. Thus, scans tend to be infrequent, and changes are often not immediately noted or treated.
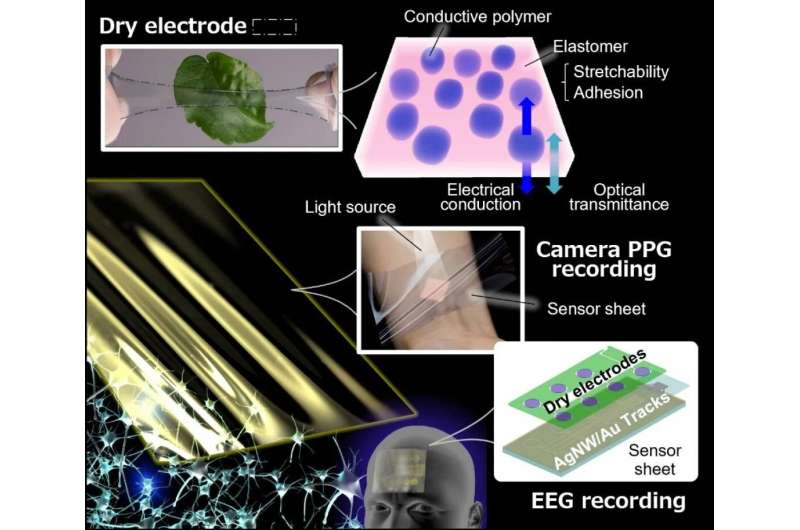
To combat these problems, the development of small wearable devices using electroencephalography—where electrodes measure electrical activity on the scalp as an estimate of the underlying brain activity—has recently begun. However, such devices are usually painful when worn long-term and often have low signal-to-noise ratios, which limits their sensitivity. The research team at Osaka University thought that they might be able to do better.
“We were able to fuse together organic and inorganic materials to create a stretchable and transparent sensor sheet that can be worn on the forehead, is gentle to the skin, and is invisible to the eye,” says lead author of the study Teppei Araki. “Unlike conventional wearable devices, our multifunctional electrode system has medical device-like performance, is easy to apply, and is comfortable to wear for long periods of time.”
The performance of their device was so good that the researchers were able to conduct sleep-stage classification, which requires very clear brain activity readings. Another highlight of the device was its stickiness—it remained in place during a range of different activities during the testing process, although the research team admits they still need to work on its adhesion during activities that cause a lot of sweating.
“One other key advantage of our sensor sheet is its range of possible applications,” explains Tsuyoshi Sekitani, senior author of the study. “It can potentially be used to remotely assess many other health indicators, such as electrocardiograms, pulse waves, blood oxygen saturation, or blood flow.”
Given the current demand for imperceptible, wearable health sensors, the development of this new device has huge clinical and commercial potential. By measuring brain activity and other health-related factors in daily life, diseases are much more likely to be diagnosed and treated earlier, leading to positive health outcomes for millions of people worldwide.
Source: Read Full Article


