Lymphomas are a diverse group of cancers of the immune system, which is the body’s primary defense against autoimmune disease, infections, and malignancy. Now, researchers at the University of Tsukuba have clarified risk factors and molecular mechanisms underlying primary and adaptive resistance to cancer immunotherapy. This knowledge may inform treatment strategies against aggressive Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL) including Burkitt lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
One way cancer treatments fail is because malignant cells survive radiation, chemotherapy or endogenous immune surveillance by evading apoptosis. Apoptosis, or “programmed cell death,” is an ordered and orchestrated cellular suicide, executed by regulatory proteins in response to internal stress or external signals. The Fas receptor, a cell-surface death receptor, binds with its ligand FasL and activates initiator and executioner caspases that methodically degrade proteins and inexorably kill the cell. Apoptosis pathways can be blocked by inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) family proteins that directly inhibit caspase and pro-caspase. Elucidating these interlinked molecular mechanisms whereby cancer cells evade apoptosis is key to developing effective immunotherapeutic protocols.
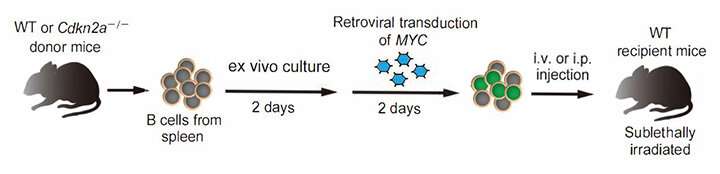
To facilitate gene manipulations and molecular analyses, the researchers first modeled mature B-cell lymphoma in syngeneic mice. “We demonstrated that Fas downregulation is required both for mature B-cell lymphomagenesis and for lymphoma cell survival,” explains Associate Professor Eiji Sugihara, lead author. “Additionally, we showed that activation of CD40 signaling, which restores Fas expression, sensitized lymphoma cells to FasL-induced apoptosis and prolonged mouse survival. Extending these findings to eleven human NHL cell lines, we confirmed that downregulated Fas expression could be restored by CD40 activation in most human cell lines, and this conferred susceptibility to Fas-mediated apoptosis in about half the cell lines studied.”
The researchers further showed that the melanoma inhibitor of apoptosis protein (Livin) promoted resistance to Fas-mediated apoptosis in lymphoma cells. Moreover, BET family proteins (specifically BRD4 and BRD2) enhance Livin expression in lymphoma cells to protect them from immune cytotoxicity. Additionally, the researchers demonstrated that BV6, an IAP antagonist that degrades Livin, extended the survival of mice transplanted with lymphoma cells previously rendered resistant to Fas-mediated apoptosis.
Source: Read Full Article