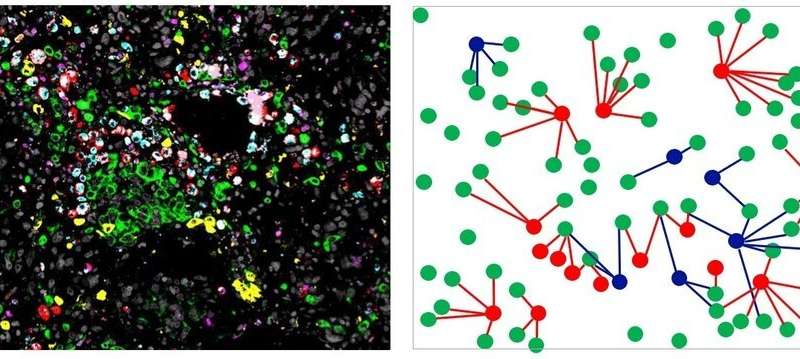
Both in the periphery and the center of lung tumors, characteristic accumulations of certain white blood cells, known as macrophages, are often found. In this case they are called tumor-associated macrophages. There are two populations with opposite effects on the tumor: while one is tumor-promoting, the second macrophage population inhibits cancer growth. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Heart and Lung Research and the Justus Liebig University in Giessen have now been able to show that identifying the position and density of the two cell populations in the tumor tissue make it possible to predict the course of the disease. This discovery may lead to new therapeutic possibilities.
Immune cells significantly influence the course of tumors. Depending on the cell type, they can both promote and inhibit tumor growth. This is particularly true for a group of macrophages, which accumulate in the tumor center or the peripheral areas in sometimes large numbers. Depending on their activation state, these so-called tumor-associated macrophages can have a positive or negative influence on the course of the disease.
Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Heart and Lung Research and the Justus Liebig University in Giessen discovered that the accumulation of a subpopulation of tumor-associated macrophages in a certain area can lead to conclusions about the further course of the tumor disease. Rajkumar Savai, project leader in the department “Development and Remodelling of the Lung” and member of the Centre for Internal Medicine at Justus Liebig University explains: “With lung tumors, it is usually possible to distinguish the center of the tumor from the peripheral area. Because a particularly large number of immune cells migrate to the latter, we refer to this area as the invasive tumor margin”.
For their study, the researchers used an elaborated microscopy technique known as multiplex immunofluorescence microscopy. By this technique, macrophages could be safely identified. Furthermore their distance from neighboring tumor cells was analyzed. In addition, the Max Planck researchers divided these cells into tumor-promoting and tumor-inhibiting tumor-associated macrophages based on certain properties. “We found that more tumor-promoting cells were found in the invasive border area of the tumor than tumor-inhibiting cells. Moreover, they were located more adjacent to the tumor cells,” said Savai. “Based on tissue samples from more than a hundred patients, we were then able to identify a pattern.”
According to this study, the survival rate in lung cancer patients was lower, in particular when the tumor-promoting macrophages in the invasive marginal areas were particularly close to the tumor cells and at the same time tumor-inhibiting macrophages were further away. The cell number also had an influence on the prognosis of the patients: “If there were fewer tumor-inhibiting macrophages in the tumor center, patients had a lower probability for surviving. Overall, we found more tumor-promoting macrophages than tumor-inhibiting macrophages,” Savai said.
Source: Read Full Article