A new research paper titled “Combined epigenetic and immunotherapy for blastic and classical mantle cell lymphoma” has been published in Oncotarget.
Classical MCL (cMCL) constitutes 6-8% of all B cell non-Hodgkins lymphoma (NHL). Despite recent advances, MCL is incurable except with allogeneic stem cell transplant. Blastic mantle cell lymphoma (bMCL) is a rarer subtype of cMCL associated with an aggressive clinical course and poor treatment response, frequent relapse and poor outcomes.
In this new study, researchers from Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine, Penn State Hershey Cancer Institute, Cassidy Cancer Center, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, National Cancer Institute, University of Virginia, UVA Cancer Center, University of Arizona College of Medicine, Oregon Health and Science University, and Beverly Hills Cancer Center treated 13 bMCL patients with combined epigenetic and immunotherapy treatment consisting of vorinostat, cladribine and rituximab (SCR).
“We report an increased OS [overall survival] greater than 40 months with several patients maintaining durable remissions without relapse for longer than 5 years,” write the researchers.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=LW81QHP1YCY%3Fcolor%3Dwhite
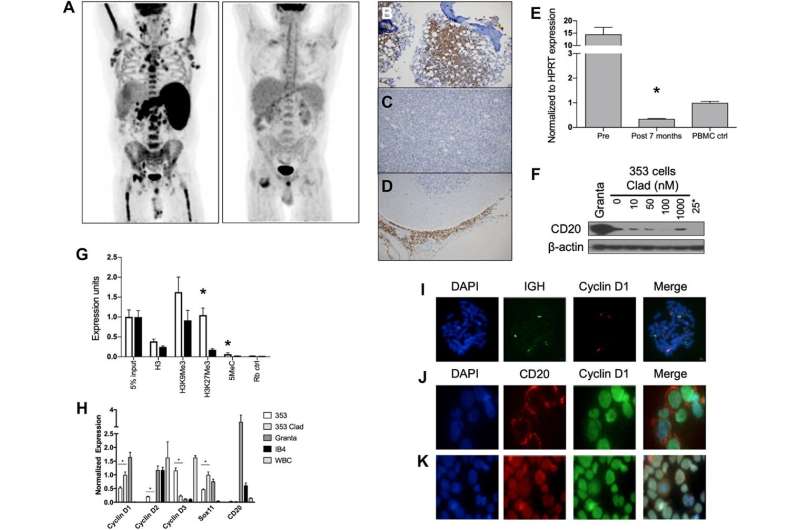
These results are remarkably better than current treatment regimens, which in bMCL, range from 14.5-24 months with conventional chemotherapy regimens. The researchers demonstrate that the G/A870 CCND1 polymorphism is predictive of blastic disease, nuclear localization of cyclinD1 and response to SCR therapy. The major resistance mechanisms to SCR therapy are loss of CD20 expression and evasion of treatment by sanctuary in the CNS. These data indicate that administration of epigenetic agents improves efficacy of anti-CD20 immunotherapies.
The researchers conclude, “This approach is promising in the treatment of MCL and potentially other previously treatment refractory cancers.”
More information:
Francis R. LeBlanc et al, Combined epigenetic and immunotherapy for blastic and classical mantle cell lymphoma, Oncotarget (2022). DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.28258
Journal information:
Oncotarget
Source: Read Full Article