A hormone called fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) protects mice against ethanol-induced loss of balance and righting reflex, according to a study publishing on March 7 in the journal Cell Metabolism.
“We’ve discovered that the liver is not only involved in metabolizing alcohol but that it also sends a hormonal signal to the brain to protect against the harmful effects of intoxication, including both loss of consciousness and coordination,” says co-senior study author Steven Kliewer of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center.
“We’ve further shown that by increasing FGF21 concentrations even higher by injection, we can dramatically accelerate recovery from intoxication. FGF21 does this by activating a very specific part of the brain that controls alertness,” says Kliewer.
The consumption of ethanol produced by the natural fermentation of simple sugars in ripening fruits and nectars can cause intoxication, impairing mobility and judgment. Animals that consume fructose and other simple sugars have evolved liver enzymes to break down ethanol.
FGF21 is a hormone that is induced in the liver by a variety of metabolic stresses, including starvation, protein deficiency, simple sugars, and ethanol. In humans, ethanol is by far the most potent inducer of FGF21 described to date. Previous studies showed that FGF21 suppresses ethanol preference, induces water drinking to prevent dehydration, and protects against alcohol-induced liver injury.
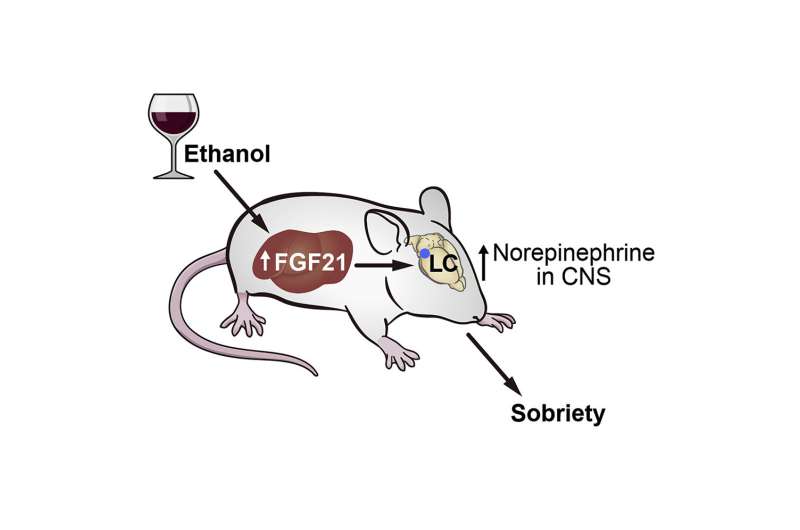
In the new study, Kliewer and co-senior study author David Mangelsdorf of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center show that FGF21 plays a broader role in defending against the harmful consequences of ethanol exposure than previously thought. In mice, FGF21 stimulated arousal from intoxication without changing the breakdown of ethanol. Mice lacking FGF21 took longer than their littermates to recover their righting reflex and balance following ethanol exposure. Conversely, pharmacologic FGF21 administration reduced the time needed for mice to recover from ethanol-induced unconsciousness and lack of muscle coordination.
Surprisingly, FGF21 did not counteract sedation caused by ketamine, diazepam, or pentobarbital, indicating specificity for ethanol. FGF21 mediated its anti-intoxicant effects by directly activating noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus region in the brain, which regulates arousal and alertness. Taken together, the results suggest that the FGF21 liver-brain pathway evolved to protect against ethanol-induced intoxication. According to the authors, this pathway may modulate a variety of cognitive and emotional functions to enhance survival under stressful conditions.
Yet it remains to be determined whether activation of the noradrenergic system contributes to FGF21’s other effects, including those on metabolism and ethanol and sweet preference. Although both FGF21 and noradrenergic nervous system activity are induced by ethanol in humans, additional studies will also be required to determine whether FGF21’s anti-intoxicant activity translates to humans.
“Our studies reveal that the brain is the major site of action for FGF21’s effects,” Mangelsdorf says. “We are now exploring in greater depth the neuronal pathways by which FGF21 exerts its sobering effect.”
More information:
Steven A. Kliewer, FGF21 Counteracts Alcohol Intoxication by Activating the Noradrenergic Nervous System, Cell Metabolism (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.02.005. www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/f … 1550-4131(23)00041-4
Journal information:
Cell Metabolism
Source: Read Full Article


