A new research paper was published in Genes & Cancer entitled “Ectopic expression of lncRNA MVIH as a potential diagnostic biomarker in cervical cancer.”
Cervical cancer (CC) is one of the most common cancers in women. Recent advances in screening and vaccination against the papilloma virus (HPV) have increased protection against CC. However, there is no effective diagnostic biomarker and treatment approach during the course of the disease.
In this new study, researchers Mohammad Ghanbari, Aida Aghazadeh, Elaheh Malekabbaslou, Ali Rajabi, Aref Sobhkhizy, Melika Maydanchi, Ali Saber, and Reza Safaralizadeh from the University of Tabriz and Zimagene Medical Genetics Laboratory aimed to evaluate the changes in the expression of lncRNA associated with microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma (lncRNA MVIH) and its diagnostic value as a biomarker in CC patients.
“This research is aimed to evaluate the expression levels of MVIH in CC tumors to assess the potential of this lncRNA as a diagnostic biomarker in CC patients,” they write.
One-hundred and fifteen (n = 115) pairs of CC primary tumor and marginal non-tumor tissue samples were obtained from Tabriz Valiasr International Hospital (Tabriz, Iran).
https://youtube.com/watch?v=JHeZNGBEPGY%3Fcolor%3Dwhite
RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis followed by quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR (qRT-PCR) were considered to investigate alterations in the expression levels of MVIH in patients with CC. The associations between MVIH expression changes and clinicopathological features as well as its potential as a diagnostic biomarker were assessed using SPSS and GraphPad prism software and the receiver operating characteristic (ROC).
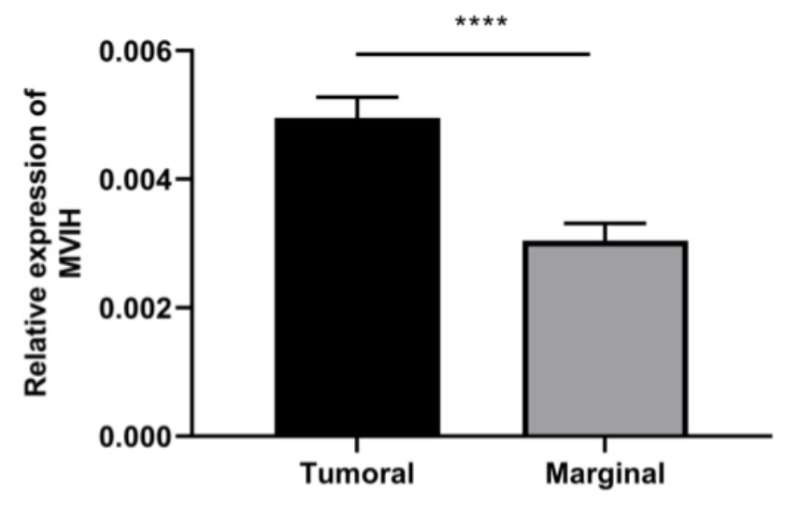
The expression levels of MVIH were significantly higher in CC tumors as compared to marginal non-tumor samples (p < 0.0001). Overexpression of MVIH was significantly associated with younger age (p = 0.033), lymph node metastasis (p = 0.031), tumor invasion depth (p = 0.035), and squamous cell type of CC (p = 0.019). The ROC analysis for MVIH as a diagnostic biomarker revealed the respective sensitivity and specificity of 67.83 and 80.
Source: Read Full Article