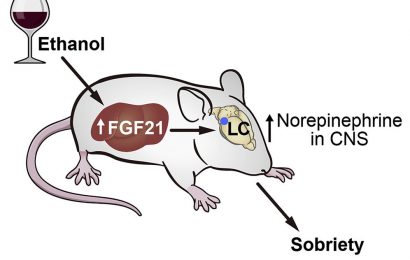
Since 1949, lithium has been a mainstay for treating bipolar disorder (BD), a mental health condition marked by extreme mood swings. But scientists still don’t have a clear understanding of how the drug works, or why some patients respond better than others. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science developed a method for imaging lithium in living cells, allowing them to discover that neurons from BD patients accumulate higher levels of lithium than healthy controls.
According to the National Institutes of Health, 4.4% of U.S. adults experience BD at some time in their lives. Studies have shown that lithium-based drugs can help stabilize mood and reduce suicide risk in people with BD. However, only about one-third of BD patients respond completely to lithium treatment, and the rest respond only partially or not at all. One reason could be that the drug has an extremely narrow therapeutic range: Below a certain blood serum level of lithium, most patients do not respond, but at a slightly higher level, they can experience severe side effects. Being able to measure lithium concentrations directly in a patient’s neurons could help scientists understand how lithium works as a drug, and then they could use this knowledge to optimize the dosage. So Yi Lu and colleagues wanted to develop a method to detect and measure lithium in living cells at therapeutically relevant concentrations.
Source: Read Full Article