A research team led by Prof. Li Hai and Wang Hongzhi from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has recently proposed an interpretable radiomic model for predicting radiotherapy treatment response in patients with brain metastases. Results were published in European Radiology.
Radiometrics refers to the extraction of high-throughput radiological features from medical images to assist clinical decision making. These radiological features can reflect the biological information of tumors that cannot be directly obtained by traditional image interpretation. Therefore, machine learning-based approaches can rely on in-depth data mining to gain additional knowledge about tumor heterogeneity. At present, there is no model to accurately predict the efficacy of radiotherapy in patients with brain metastases in clinical practice.
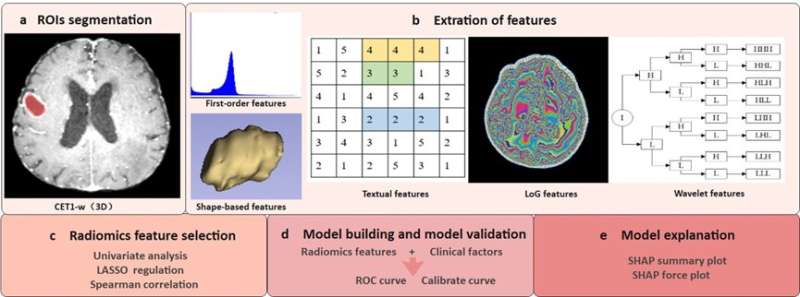
In this study, combining radiomics and SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) methods, the researchers proposed the interpretable radiomic model to solve this clinical problem.
They extracted radiomic features from the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images of patients with brain metastases before radiotherapy. Then, they used machine learning methods to model the radiation. Finally, they interpreted the model using SHAP based on game theory, which could help develop precise radiotherapy for patients with brain metastases.
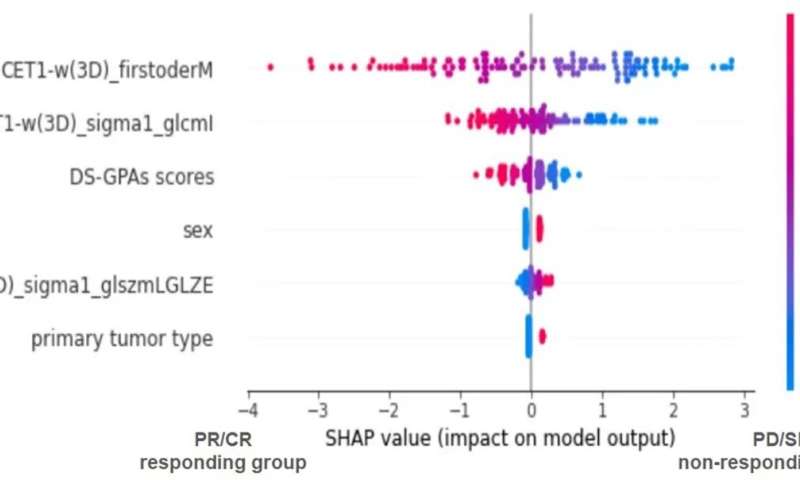
The model has good performance, and the prediction results of external validation group also show that the model has generalization to a certain extent, according to Wang Yixin, first author of the study.
Source: Read Full Article