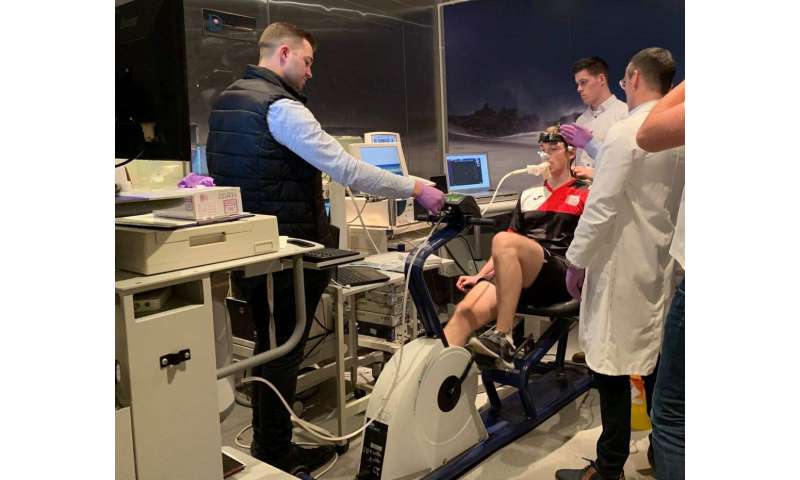
A wearable biosensor may help monitor stress experienced by healthcare professionals, according to a study published in Physiological Reports.
In the study of 12 healthy male volunteers, a wearable biosensor that is placed on the chest, called the VitalScout, provided an accurate assessment of physiological parameters—heart rate and respiration rate—that are used to calculate stress. Furthermore, the biosensor’s metrics correlated strongly to those obtained using breathing analyses, and they could discriminate changes associated with stress from changes related to increased physical activity.
Source: Read Full Article


