According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology, diagnostic performance of LR-5 for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) diagnosis was not significantly different between modified contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) using perfluorobutane and CT/MRI LI-RADS version 2018.
“The findings support the application of modified CEUS criteria using perfluorobutane for diagnosing HCC in high-risk patients,” wrote Jianhua Zhou, MD, Ph.D., of Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center’s State Key Laboratory of Oncology in Guangzhou, South China.
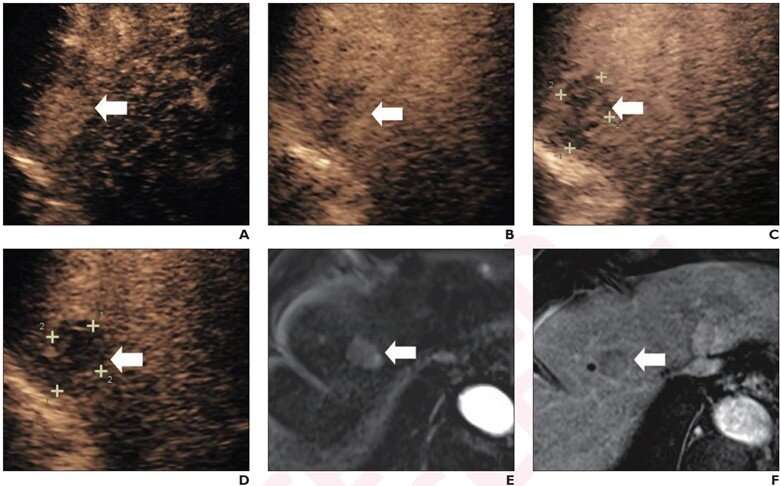
171 patients (140 men, 31 women; mean age, 54 years) at high risk for HCC with a pathologically confirmed liver observation were evaluated by both CEUS using perfluorobutane and contrast-enhanced CT or MRI, between March 2020 and May 2021. A matching algorithm was used to select 2 patients with HCC for each patient with a non-HCC lesion.
Two readers evaluated observations using proposed modifications to CEUS LI-RADS version 2017 that classify certain observations as LR-5—rather than LR-4 or LR-M, based on presence of defect post-perfluorobutane administration.
Ultimately, modified CEUS criteria using perfluorobutane and CT/MRI LI-RADS v2018 showed no significant difference in sensitivity (92.1% vs. 89.5%), specificity (87.9% vs. 84.2%), or accuracy (90.6% vs. 87.7%) of LR-5 for HCC. All observations assigned LR-4 (n=5) or LR-M (n=6) by CT/MRI LI-RADS v2018 but LR-5 by modified CEUS were HCC.
“Modified CEUS criteria performed similarly as CT/MRI LI-RADS v2018 and additional HCCs in a subset of observations assigned LR-4 or LR-M by CT/MRI LIRADS v2018,” the authors reiterated.
More information:
Lingling Li et al, Intraindividual Comparison of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Using Perfluorobutane With Modified Criteria Versus CT/MRI LI-RADS Version 2018 for Diagnosing HCC in High-Risk Patients, American Journal of Roentgenology (2022). DOI: 10.2214/AJR.22.28420
Journal information:
American Journal of Roentgenology
Source: Read Full Article