A team of researchers led by Dr. Pensée Wu, senior lecturer at Keele University’s School of Medicine, have found that women who conceive with assisted reproductive technology such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) are at a higher risk of vascular and pregnancy complications.
This is the first population-based study of its kind and the largest analysis to consider both pregnancy outcomes and vascular complications at the time of delivery for women who have conceived using assisted reproductive technology (ART).
Assisted reproductive technology refers to treatments that are used to improve the odds of conception which are a common treatment option for infertility, a problem which affects an estimated 48 million couples worldwide.
Researchers analyzed the data of more than 34 million hospital births from the U.S. National Inpatient Sample database to assess patient characteristics, pregnancy outcomes and vascular complications.
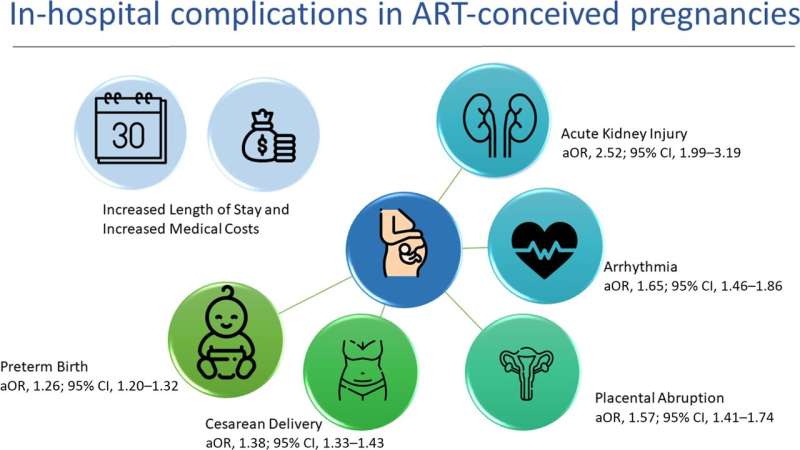
The team discovered that women who conceived with ART were more than twice as likely to suffer kidney failure and have a 65% higher risk of an irregular heartbeat. Findings also highlighted that ART pregnancies were more likely to be associated with placental abruption, a serious condition in which the placenta starts to come away from the inside of the womb wall, as well as cesarean and preterm births.
The study, published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, found that women who became pregnant with ART were on average older than those who conceived spontaneously, with a median age of 35 years old compared to 28 years old. They were also found to have more pre-existing health conditions, including obesity and cardiovascular disease.
The research highlights the importance of pre-pregnancy counseling from healthcare clinicians on the associated complications of ART.
Source: Read Full Article